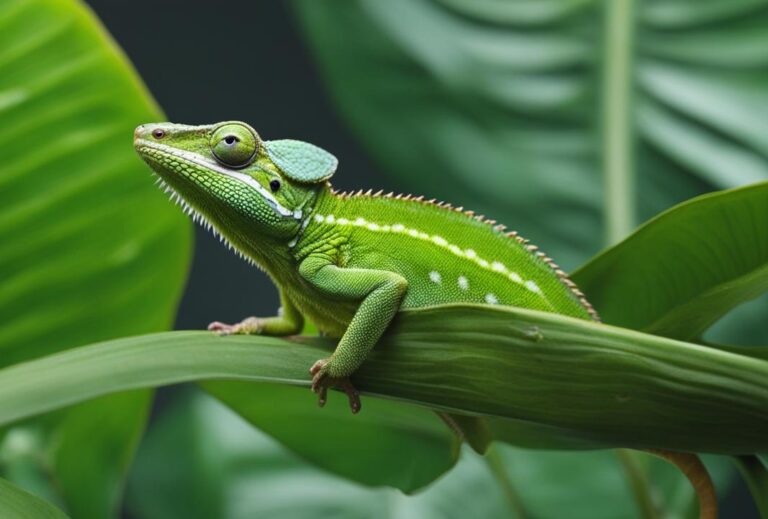
Why Do Chameleons Eat Their Shed Skin?
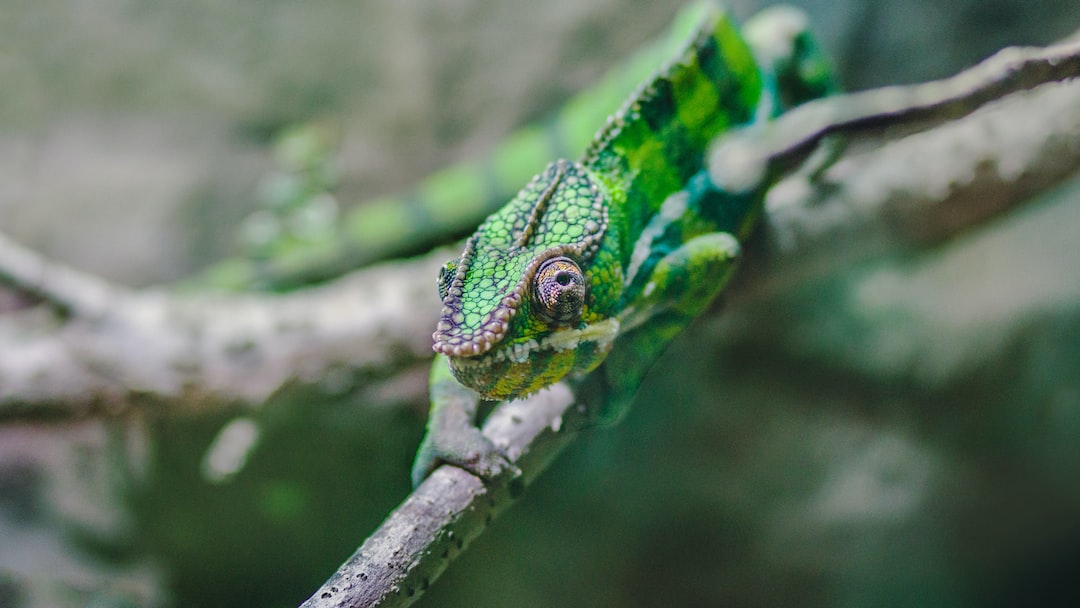
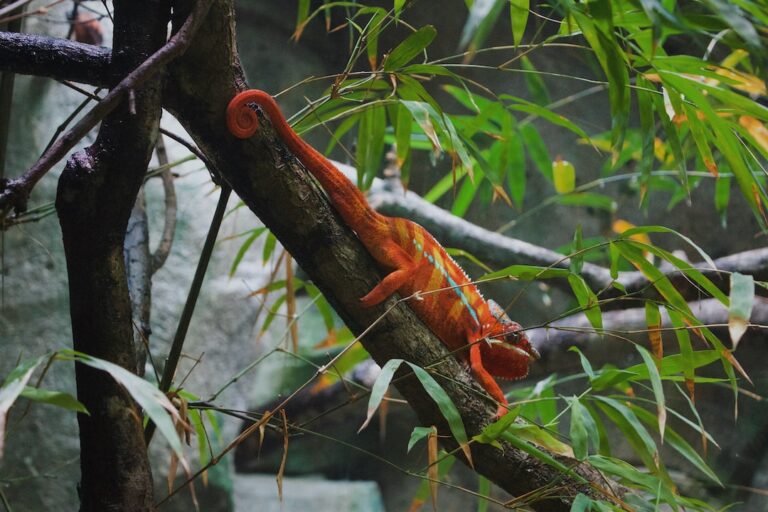
Chameleons are fascinating creatures known for their ability to change color and blend into their surroundings. They are unique reptiles that belong to the family Chamaeleonidae and are found in various parts of the world, including Africa, Madagascar, and parts of Asia and Europe. Chameleons have a number of distinctive characteristics that set them apart from other animals, such as their independently moving eyes, prehensile tails, and specialized feet for climbing. One aspect of chameleon biology that is particularly intriguing is their feeding habits, which differ significantly from those of other animals.
Table of Contents
Shedding Skin: What Happens and Why It’s Important
Shedding skin, also known as molting or ecdysis, is a natural process that chameleons undergo to replace their old skin with a new one. This process is essential for chameleons to maintain healthy skin and promote growth. Shedding occurs periodically throughout a chameleon’s life as it grows and develops. During shedding, the outer layer of the skin, known as the epidermis, is shed off to reveal a fresh layer underneath.
The shedding process begins with the chameleon’s skin becoming dry and flaky. The old skin then starts to separate from the new skin underneath, forming a layer that can be easily peeled off. The chameleon will often rub against branches or other surfaces to help remove the old skin. Once the shedding is complete, the chameleon’s skin will appear vibrant and healthy.
The Nutritional Value of Chameleon Skin
Chameleon skin is not only important for protection but also provides essential nutrients for these reptiles. Chameleon skin contains a variety of nutrients that are vital for their overall health and well-being. These include proteins, vitamins, minerals, and amino acids. The nutritional value of chameleon skin is comparable to that of other food sources for chameleons, such as insects and plants.
Proteins are essential for growth and development, as well as for maintaining healthy skin and muscles. Chameleon skin is rich in proteins, which provide the necessary building blocks for these processes. Vitamins and minerals found in chameleon skin, such as vitamin A and calcium, are important for maintaining strong bones, healthy eyesight, and a robust immune system. Amino acids, which are the building blocks of proteins, are also present in chameleon skin and play a crucial role in various physiological processes.
How Chameleons Consume Their Shed Skin
Chameleons have a unique way of consuming their shed skin. After the shedding process is complete, the chameleon will often eat the discarded skin. This behavior is known as dermatophagy. Chameleons use their long, sticky tongues to capture and consume the shed skin. The tongue is rapidly extended to catch the skin and then retracted back into the mouth.
The process of eating shed skin serves several purposes for chameleons. Firstly, it helps them clean their environment by removing any traces of shed skin that may attract predators or parasites. Secondly, consuming shed skin provides chameleons with additional nutrients that they may not obtain from their regular diet. Lastly, eating shed skin helps chameleons maintain a healthy digestive system by providing roughage that aids in digestion.
The Benefits of Eating Shed Skin for Chameleons
There are several benefits to chameleons consuming their shed skin. One of the main advantages is that it helps them maintain a balanced and nutritious diet. Shed skin contains essential nutrients that are beneficial for chameleon health, including proteins, vitamins, minerals, and amino acids. By consuming their shed skin, chameleons can supplement their regular diet and avoid nutrient deficiencies.
Another benefit of eating shed skin is that it helps chameleons maintain healthy skin and promote growth. The nutrients found in the shed skin contribute to the development of new skin cells and support the overall health of the chameleon’s skin. This is particularly important for chameleons, as their skin plays a crucial role in thermoregulation, protection against predators, and communication with other chameleons.
Shedding Skin as a Way to Eliminate Toxins
Shedding skin is not only important for maintaining healthy skin and growth but also serves as a way for chameleons to eliminate toxins from their bodies. As chameleons shed their old skin, any toxins or waste products that may have accumulated in the skin are also removed. This process helps to detoxify the chameleon’s body and maintain overall health and well-being.
Toxins can accumulate in the skin through various means, such as exposure to pollutants or ingesting contaminated food. By shedding their skin, chameleons can effectively eliminate these toxins and prevent them from building up in their bodies. This detoxification process is essential for chameleon health and ensures that they can continue to thrive in their environment.
Shedding Skin as a Way to Regulate Body Temperature
Shedding skin also plays a crucial role in helping chameleons regulate their body temperature. Chameleons are ectothermic animals, which means that they rely on external sources of heat to regulate their body temperature. The shedding process allows chameleons to remove any old or damaged skin that may hinder their ability to absorb heat from their environment.
When a chameleon sheds its old skin, it exposes a fresh layer of skin that is more efficient at absorbing heat. This enables the chameleon to effectively regulate its body temperature and maintain optimal physiological function. By shedding their skin, chameleons can adapt to changes in temperature and ensure that they remain within their preferred temperature range.
The Role of Shed Skin in Chameleon Behavior and Socialization
Shedding skin also plays a role in chameleon behavior and socialization. Chameleons use their skin as a means of communication with other chameleons. By shedding their skin, chameleons can change their appearance and display different colors and patterns. This allows them to communicate their mood, reproductive status, and dominance to other chameleons.
In addition to visual communication, shedding skin also releases pheromones that can be detected by other chameleons. These pheromones convey important information about the chameleon’s health, reproductive status, and territorial boundaries. By shedding their skin, chameleons can refresh these pheromones and ensure that their messages are effectively communicated to other chameleons.
The Impact of Shedding Skin on Chameleon Health and Well-being
Proper shedding is crucial for chameleon health and well-being. If a chameleon is unable to shed its skin properly, it can lead to a number of health issues. For example, retained shed skin can constrict blood flow and cause tissue damage. It can also create an ideal environment for bacteria or parasites to thrive, leading to infections or infestations.
Inadequate shedding can also result in nutrient deficiencies, as the chameleon may not be able to consume its shed skin and obtain the necessary nutrients. This can lead to stunted growth, weakened immune function, and overall poor health. Therefore, it is important for chameleon owners to ensure that their pets have the proper conditions and diet to support healthy shedding.
Why Chameleons Eating Their Shed Skin is a Fascinating and Important Aspect of Their Biology
In conclusion, the process of shedding skin is a fascinating and important aspect of chameleon biology. It allows these reptiles to maintain healthy skin, promote growth, eliminate toxins, regulate body temperature, and communicate with other chameleons. Eating shed skin provides chameleons with additional nutrients and helps them avoid nutrient deficiencies. Proper shedding is crucial for chameleon health and well-being, and it is important for chameleon owners to understand and support this natural process. By appreciating the unique biology of chameleons, we can better care for these incredible creatures and ensure their long-term health and happiness.
If you’re interested in the eating habits of reptiles, you might also want to check out this article on “Do Iguanas Eat Rats?” It explores the dietary preferences of iguanas and whether or not they consume rats as part of their natural diet. Click here to learn more about this fascinating topic.